14 Common Internet Terms Everyone Should Know
August 10th, 2021 | Rural Broadband by Gravity

Find Internet jargon a bit much sometimes? We’re here to break down the nitty gritty terms in a way that even your grandma could understand. Take 5 mins to read our jargon buster below and see how many you actually know. You might be surprised at what you learn.
What is '4G'?

4G stands for fourth generation of broadband cellular network technology and it’s called that because it’s the fourth generation of mobile technology. 4G is a type of mobile phone reception that you can get when you are close to a 4G capable (newer) cell tower. It’s much faster than 3G. In fact, it’s so fast that it can even be used as a way of getting broadband to your home computer. You’ll know if you have 3G or 4G coverage by looking at the top right of your mobile phone screen next to your coverage bars (it’ll say ‘3G’ or ‘4G’).
What is '5G'?

5G is the newest mobile phone reception type that offers increased speeds faster than 4G. It’s exceptionally fast but can only be accessed if you are close to a 5G capable cell tower, which have mostly been reserved to urban areas at the moment.
What is a 'Fibre' broadband connection?
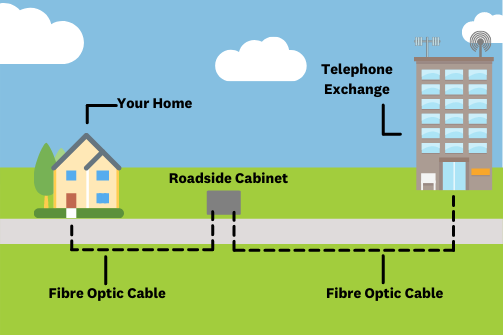
Fibre is a specialised cable that is installed underground and leads to your house. Once it’s setup, you can get extremely fast internet. Before fibre, an internet connection used your phone line, but this was slow and could interrupt your phone service. Not everyone can get fibre, it depends on where you are on the list of towns that are getting it installed (it’s going to take years and years and even then, not everywhere will be covered).
What is a 'Wireless Internet' Connection?
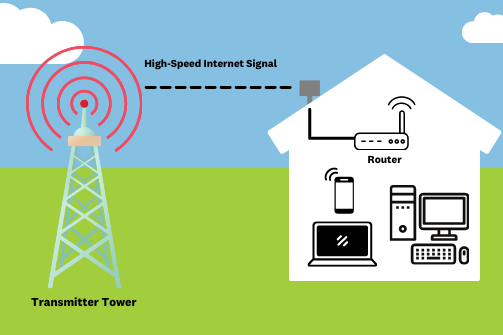
Wireless internet, as its name suggest, doesn’t use cables or wires (like fibre or your telephone line). It most often refers to internet being transmitted to you from a cell phone tower. In many cases the phone tower is beaming 4G mobile internet to a wireless receiver at your house. The wireless receiver pushes the connection to your router inside your home and tadaaaa your devices can get internet. Local providers called WISPs (Wireless Internet Service Providers) also provide a Wireless Internet service outside of a 4G connection but still delivered via local towers.
What is an 'ADSL' Internet Connection?
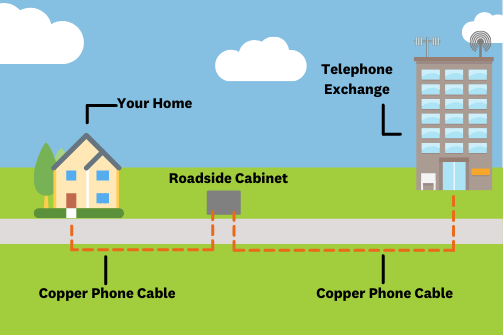
ADSL stands for “Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line”. You probably don’t need to remember that (unless it comes up in a pub quiz), what you do need to know is that ADSL uses copper telephone wires for transmitting digital information such as data, audio, and video. Simply put, it’s the old school way of connecting you to the Internet before fibre was a thing.
'Wi-Fi' Briefly Explained

Wi-Fi is the wireless technology used to connect computers, tablets, smartphones, and other devices to the internet. To set ‘Wi-Fi’ up in your home, you need a ‘Wi-Fi’ capable modem or router (the box that lets you connect to the internet). Your modem should come with instructions (or if not just look on the back of it), with the name of your “Wi-Fi Network”. You’ll be able to access the internet from any device by going to your ‘Wi-Fi Network Settings’ and selecting the name of the specific network and logging into it.
What is 'Rural Broadband'?

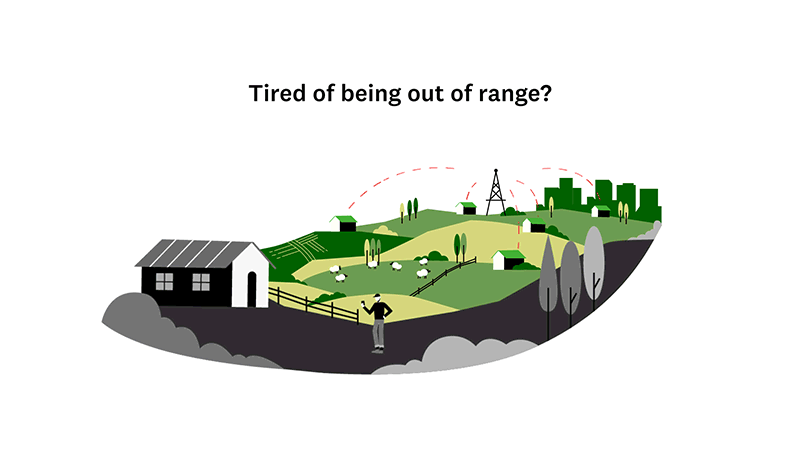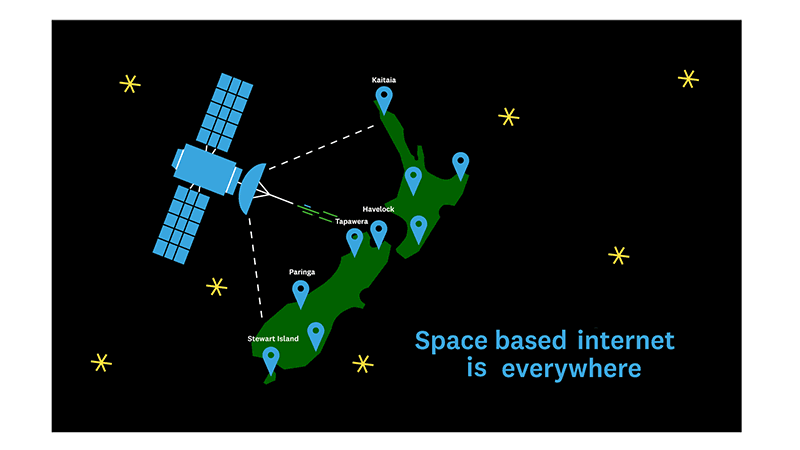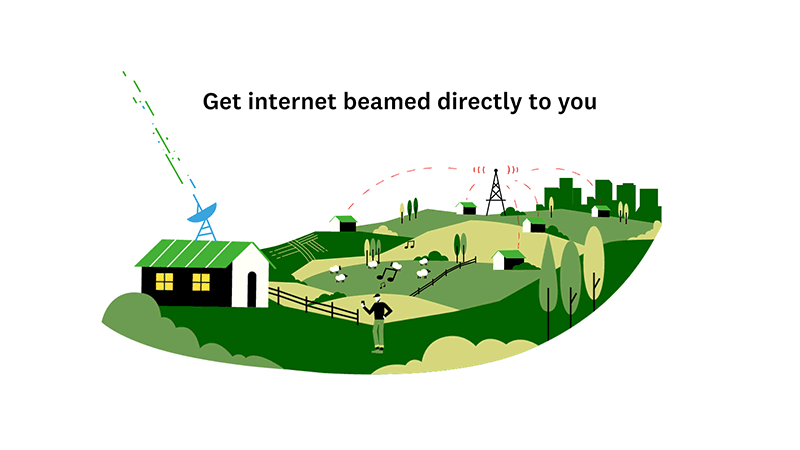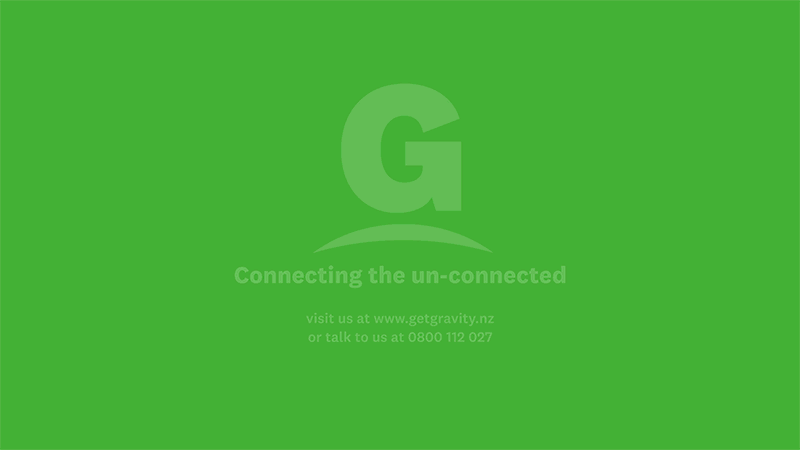
If you live rurally, you most likely can’t get high speed internet connection types like fibre. At best you might be able to get slow internet through your telephone wires. People have started using the term ‘rural broadband’ as way of describing all the types of internet that help rural living people get connected to the internet (such as Wireless Internet, 4G Internet or Satellite Internet).
'Bandwidth' Briefly Explained
Bandwidth is another word for the capacity of your internet connection and is like a road between you and your internet provider. Your internet provider only has a limited amount of bandwidth, like a road with limited lanes. Because the road has limited lanes, traffic tends to slow down when there are loads of cars. This is the same as the internet, when lots of people are using it, it gets congested and slows down for everyone. This is why you will notice your internet speeds slowing down in peak times (6-10pm).
'Mbps' Definition

Mbps stands for “megabits per second.” It is a measure of how fast the download or upload rate of your internet connection is. The higher the number the faster your internet will feel. Different internet plans will often charge differently based on the ‘Mbps’ speed. Your download and upload speed can be tested using an internet speed test.
What is an 'IP Address' and Do I Have One?

IP Address stand for “Internet Protocol Address”. This is the unique number that your internet provider assigns your connection to easily identify you and connect you to the internet. If you are connected to the internet, then you will automatically be assigned an IP address. It’s easy to find out what it is, just Google ‘What’s My IP Address’.
Online 'Streaming' Explained

About 5 or more years ago most people would ‘download’ a physical copy of a movie or song onto their computer. The downside to this is that it takes up storage space on your computer. Streaming on the other hand does not permanently download files to your computer, which is great for not clogging up your storage. Streaming temporary downloads your movie or song into a platform like your web browser (Chrome, Edge), music player (Spotify, Apple Music) or video player (Netflix, Neon, TVNZ). Once you are finished and you close it, the file is gone. Streaming does however use your ‘download data’, even if you don’t end up storing the physical file.
What Does 'Downloading' and 'Uploading' Mean?
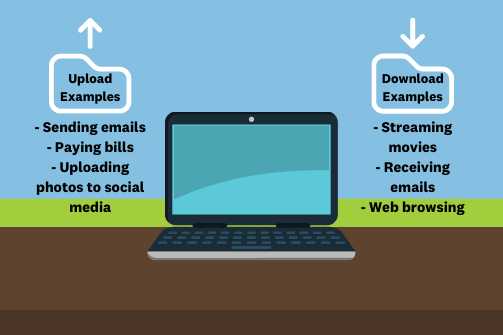
Download refers to any data that your internet connection retrieves from the internet. This includes loading websites on your browser, streaming, or saving files from the web to your device. Absolutely ANY content that comes into any of your internet connected devices is a Download.
Upload refers to any data that your internet connection sends from your connected devices to the internet or directly to another person over the internet. This includes sending an email, sending an image/message, video calling, uploading a photo or video to social media. Absolutely ANY content that is sent from any of your internet connected devices is an Upload.
What is a 'Speedtest'/'Speed Test'?
A speed test is an online tool for measuring your download speed and upload speed.
'Latency' ('Ping') Explained

Latency (also known as Ping) is the time it takes for data to be transmitted from your device to a server on the Internet and back to your device again. The lower the latency the more ‘real time’ your flow of data is. This is crucial for internet activities that need instantaneous reaction times (online games like Call of Duty and Fortnite, or bidding on the stock market). You will easily identify high latency when there is a delay (lag) between speaking to someone on a video call and them actually hearing it. Most general internet activities like browsing the web or streaming content on Netflix, aren’t affected by latency.
In summary, the internet has many terms to get your head around. With our easy to understand explanations we hope you have learnt something new. If you found this helpful, you will really enjoy finding out about the Four Surprising Internet Myths that are Fooling Rural New Zealand.
If you are living rural and want learn more about your best options then we highly recommend reading about The State of Rural Broadband in New Zealand.
Still wanting to learn something new. How about learning about how satellite internet works?